We will see the key difference between the Microprocessor and the Microcontroller.
So,
visually if you see any microcontroller or microprocessor, there is hardly any difference between them.
They almost look very identical.
But they are different in many aspects.
They are different in terms of the applications in which they are used.
They are different in terms of the cost.
They are different in terms of the processing power which they possess.
And they are different in terms of the power consumption.
So, today we will see the difference between the microprocessor and the microcontroller based on all these aspects.
So, first let's see the difference between them in terms of the applications in which they are used.
So, the classic example of the microprocessor application is personal computer or laptop.
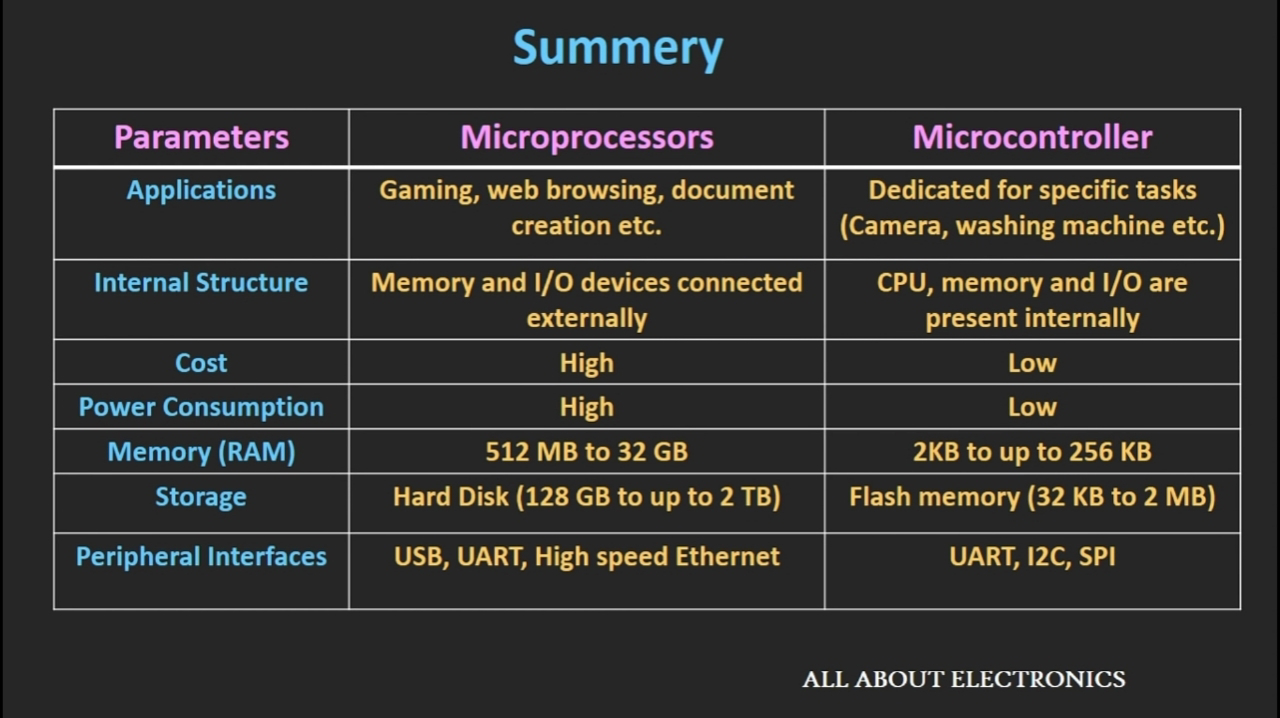
So, using this laptop we can do a lot of stuff. Like, we can use it for the gaming, for web browsing, for photo editing, for creating documents, or we can use if for mathematical calculations, simulations or media streaming.
Applications of Microprocessor -
So, the microprocessor is basically used in an application where the task in not predefined. It depends on the user.
Or it is used in applications where intensive processing is required.
While in a case of a microcontroller, they are used for specific task.
So, based on the inputs which are given to the microcontroller, it does some processing and it gives the result as an output.
So, here the input could be a user input or the inputs which are coming from the sensors.
So, the example of microcontroller applications is the digital camera, washing machine, and microwave oven.
So, if you see all these devices, the task which is going to be performed is predefined.
Like, in the case of a microwave oven, once you set the power and the timing, it gives you the cooked food.
Likewise in the case of a washing machine, once you set the parameters of the machine, it gives you the clean and dry clothes.
So, basically, a microcontroller is used in applications where the task is predefined.
Now, let's see the difference between them in terms of the internal structure.
So, like I said earlier, the microprocessors are used in applications where the task is not predefined.
Applications of Microcontroller -
So, they can be used for a very light application like creating documents or a very intensive application like gaming or media streaming.
So, the amount of memory that is required depend upon the application. So, if you see the microprocessor chip, it only contains CPU. which is Central Processing Unit.
And all the memory elements and the I/O interfaces are connected to it externally.
Internal Structures -
So, in a case of a microprocessor, memory elements like RAM, ROM, I/O ports, Serial interfaces and timers, all are connected externally.
While in a case of a microcontroller, as they are used for a specific task, the amount of memory and the I/O ports which are required are limited.
So, in a case of a microcontroller, all the memory elements and I/O ports are integrated along with the CPU inside a single chip.
So, the size of an overall system is much smaller.
While in a case of a microprocessor, as all the memory elements and I/O ports are connected externally, so overall size of the system is larger than the microcontroller.
Processing Power and Memory -
Now, let's see the difference between microcontroller and microprocessor in terms of the processing power and memory.
So, microprocessors are operated at much higher speed.
So, if you see the clock speed of a microprocessor, it is in the range of Giga Hertz.
The clock speed varies from the 1 GHz to the 4 GHz for the high-end processors.
So as microprocessor has to run an operating system, the amount of memory that is RAM and ROM, which is required is quite high.
So, if you see the Random Access Memory or RAM which is a volatile memory in the microprocessor, it ranges from 512 MB and it goes up to 32GB for high-end microprocessors.
Similarly, if you see the ROM in the microprocessor, it ranges from the 128 GB and it goes up to the 2TB.
That is 2 Tera Bytes.
And the common peripheral interfaces which you see in the microprocessors are like USB, High-speed Ethernet, and the UART.
While in a case of a microcontroller, the clock speed is in the range of Mega Hertz.
So, if you see the clock speed of microcontrollers, it ranges from the 1 MHz and it goes up to the 300 MHz in the high-end microcontrollers.
And as these microcontrollers are defined for a specific task, the amount of memory that is required by them is quite less.
So, if you see a Random Access Memory or RAM inside the microcontroller, it is in the range of Kilo Bytes.
So, it can go from the 2 KB up to the 256 KB.
Similarly, if you see a flash memory or a programme memory inside the microcontroller, it varies from the 32 KB and it can go up to the 2 MB.
And the common peripheral interfaces which you find inside the microcontroller are I2C, SPI, and UART.
So, basically all these are serial interfaces, which you find in a modern day microcontrollers.
So, if you see a modern day microprocessors, they are either 32 bit or 64 bit.
So 32-bit microprocessor means, a microprocessor can handle 32 bits of binary data at the same time.
Power Consumption and Cost -
Similarly, a 64-bit microprocessor can handle 64 bits of data at the same time.
So, in a case of 64 bit of microprocessor, all the address bus and the data buses are of the 64 bits.
Similarly, in the case of a 32-bit microprocessor, the address and the data bus are of 32 bits.
While if you see modern day microcontrollers, they are either of 8 bits, 16 bits or 32 bits.
Summary -
So, the amount of data which can be handled by a microprocessor in a single cycle is higher than the microcontrollers.
Now, let's see the difference between the microcontroller and microprocessor in terms of the power consumption and the cost.
So, in the case of a microprocessor, as all the memory elements and I/O ports are connected externally, the overall cost of the system, as well as power consumption, is higher compared to the microcontrollers.
So, this is summery of difference between the microprocessor and a microcontroller based on the various parameters which we have already discussed.
When I was discussing the application of microprocessor, I had given the example of a personal computer.
But I didn't mention anything about the smartphone.
But if you see the smartphone, it can do almost all the things which personal computer can do.
Like you can play games, you can do web browsing, you can create the documents etc. on the smartphone.
But still, it is not an example of a microprocessor.
Because the chip that you find inside the smartphone is neither microprocessor nor microcontroller.
It is sort of combination of both things.
And it is known as Sytem On Chip or SOC.
So we will discuss about it more in the upcoming posts.
So, I hope you understood the difference between the microprocessor and microcontroller.
Thank You.......



















0 Comments